所属:Osaka University
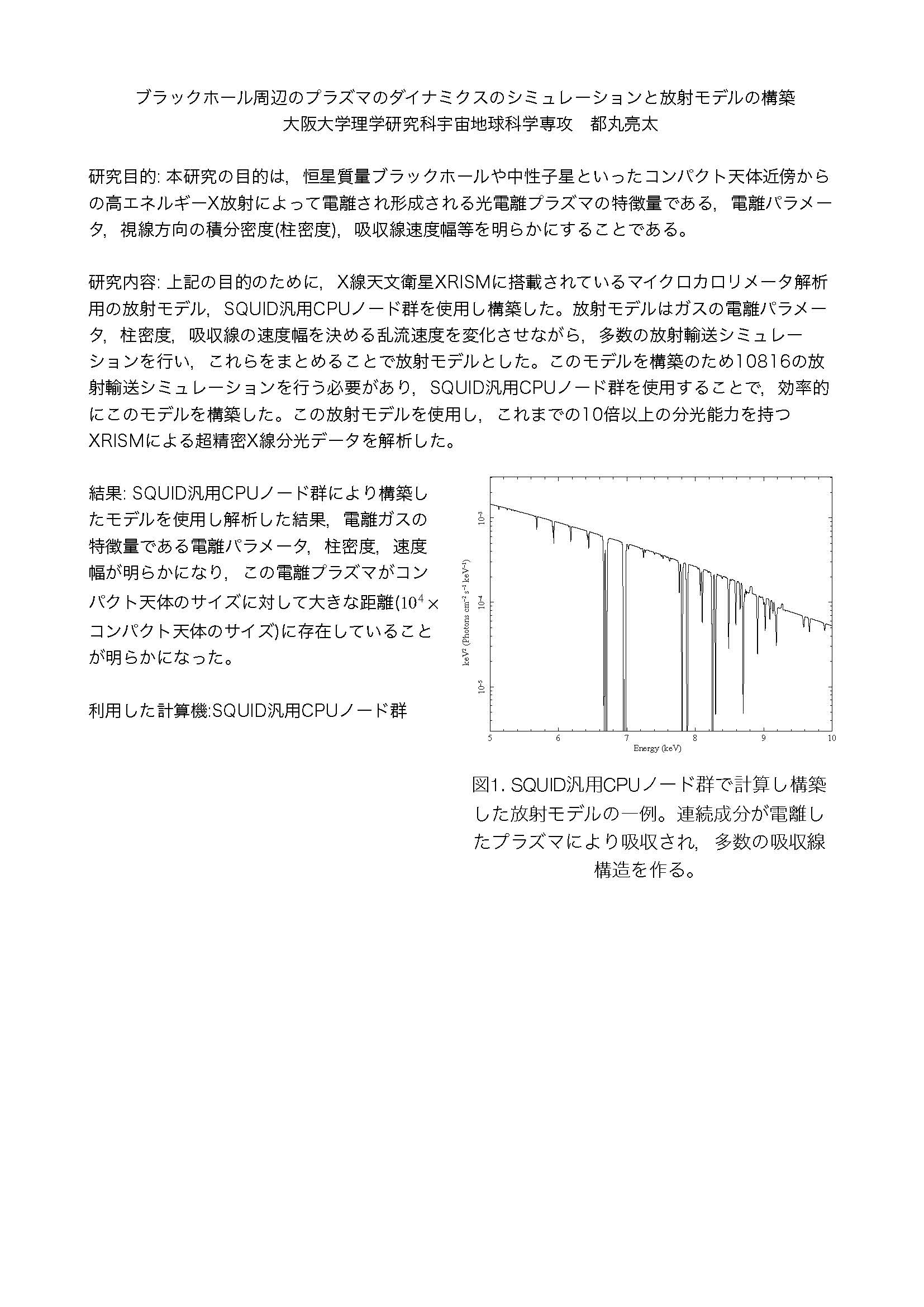
概要:The aim of this study is to elucidate the characteristic parameters of photoionized plasmas—such as the ionization parameter, the line-of-sight integrated density (column density), and the absorption line velocity width—that are formed by X-ray irradiation from the vicinity of compact objects such as stellar-mass black holes and neutron stars. To achieve this objective, we constructed a radiative model using the microcalorimeter analysis framework onboard the XRISM X-ray astronomy satellite in conjunction with the SQUID general-purpose CPU node cluster. This model was developed by performing numerous radiative transfer simulations while varying key parameters, including the gas ionization parameter, column density, and the turbulent velocity (which determines the absorption line velocity width), and by integrating the outcomes of these simulations. In total, 10,816 radiative transfer simulations were conducted, and the use of the SQUID CPU node cluster enabled the efficient construction of the model. This radiative model was then applied to analyze ultra-precise X-ray spectroscopic data obtained by XRISM, which offers more than a tenfold improvement in spectroscopic capabilities compared to previous instruments.
Posted : 2025年03月31日