Editor such as emacs and vi is available for making and modifying your program on the frontend node.
In the case that you prefer to make and edit your source code on your local PC, you need to transfer it to the frontend node before compilation.
The source code made on any windows platform needs to be transfered to the frontend node under "text" transfer mode, after saving it with character code "UTF-8" and Linefeed code:"LF".
This is important because the character code of windows platform is different from the one of the frontend node.
This page explains emacs and vi on the frontend node.
emacs
emacs is a popoular text editor with rich functionality, which users can add your customization.
Its operation is features with the short-cut operation using Ctrl key and Meta key.
"Meta key" is "Alt key" or "Esc key" actually. Here, we will use "Meta key" below.
** Ctrl-x:keep pusing Ctrl key adn then push x key.
Below is the basis usage of emacs.
1. Starting emacs
% emacs -nw [file name] (enter)
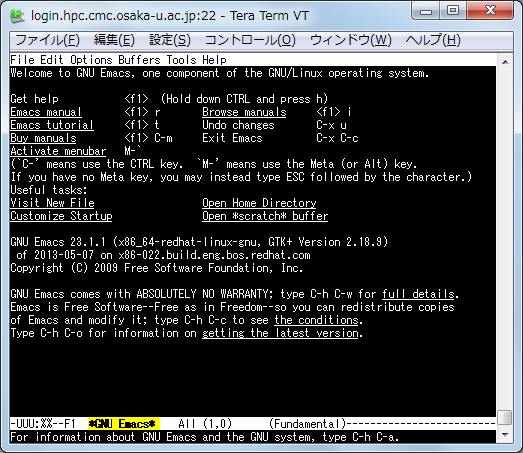
This is the snapshot when emacs was invoked with no file.
2. Editting a file
You can edit the speficied file as you like in the case that you start emacs by specifying it.
In the case that you just start emacs without specifying filename, you can open your file by using "Ctrl-x、Ctrl-f filename".
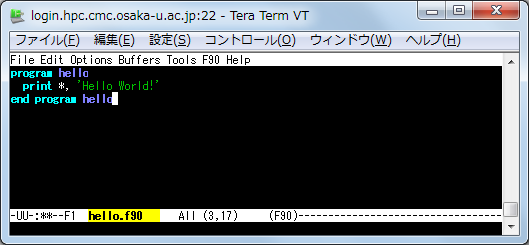
You can edit directly. Command list is below.
3. Saving file
Ctrl-x Ctrl-s
4. Terminating emacs
Ctrl-x Ctrl-c
Other useful commands is below.
"F1 key" +"t": you can star tutorial on emacs. This may be useful for novice users.
vi
vi is UNIS standard text editor.
A feature of vi is that it has two modes: "edit mode" and "command mode".
The fomer mode allows you to type characters in and the latter allows you to type commands in.
"i" key is used for switching "command mode" to "edit mode", "Esc" key for switching "edit mode" to "command mode".
Below shows the basic usage of vi.
1. starting vi
% vi [filename] (enter)
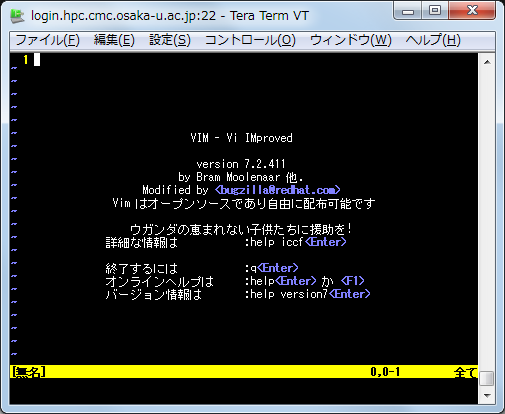
Snapshot right after starting vi without speficying filename
2.Editing
You can move "edit mode" typing "i" key. You can see "--挿入--" on terminal.
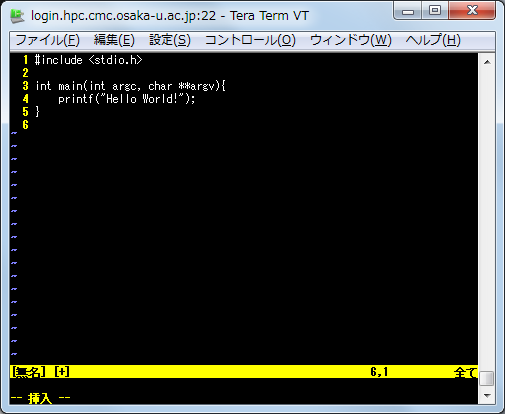
You can switch "command mode" typing "Esc" key after finishing your edit. Edit operaions such as deleting, copying, and cutting are done with the following commands.
3. Saving file
Under "command mode", type ":w". In the case that you want to specify filename, you can type you specified filename after "w".
4. Terminating
Under "command mode", type "q".
Below is the useful command list.
Command list of emacs and vi
| Function | emacs | vi |
|---|---|---|
| proceed one character | Ctrl-f(right cursor) | l(right cursor) |
| proceed back one character | Ctrl-b(left cursor) | h(left cursor) |
| move upward | Ctrl-p(up cursor) | k(up cursor) |
| move downward | Ctrl-n(down cursor) | j(down cursor) |
| proceed one word | Meta-f | w |
| proceed one word back | Meta-b | b |
| move start of line | Ctrl-a | 0 |
| move end of line | Ctrl-e | $ |
| proceed one screen | Ctrl-v | Ctrl-f |
| proceed one screen back | Meta-v | Ctrl-b |
| copy | Ctrl-space key after specifying copy area Meta-w |
v after specifying copy area y |
| cut | Ctrl-space after specifying cut area Ctrl-w |
v after specifying cut area d |
| paste | Ctrl-y | p |
| Undo | Ctrl-_ | u |
| cancel operation | Ctrl-g | Esc |
| termination without saving | Ctrl-x, Ctrl-c type no when you are prompted to answer |
:q! |
| termination with saving | Ctrl-x, Ctrl-c | :wq |
| save | Ctrl-x, Ctrl-s | :w |
| save with different filename | Ctrl-x, Ctrl-w | :w filename |

